Published on Friday, 20 December 2024
As I’ve been exploring backend architectural design to improve my knowledge while building SpeedCheck, I encountered some insightful concepts that I found both interesting and educational.
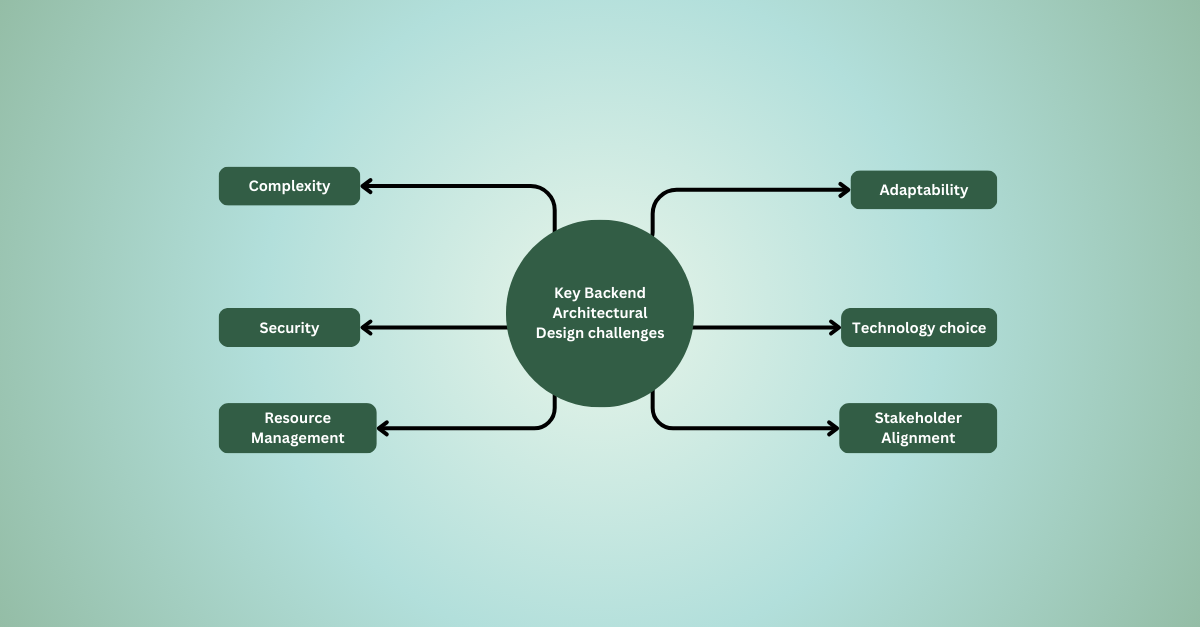
One thing that stood out is how challenging backend architecture can be, especially as systems grow more complex and involve more stakeholders. Here are some key challenges that developers often face:
1. Complexity
This is hands down one of the biggest challenges. As systems grow, their complexity tends to increase—distributed systems especially. If you have to spend 20 minutes explaining your architecture in a meeting and people still don’t get it, that’s a sign your design might be overly complicated.
To manage complexity, always keep your goals clear on the problem you want to solve. Starting simple is fine as long as your app meets the requirements you need. Overcomplicating things too soon can waste time and resources. While experimentation can be fun, it’s important to focus on building solutions that are maintainable and easy to understand.
2. Adaptability
Designing systems that can adapt to changing business needs is challenging but an important consideration. Making your system adaptable is essential to prevent overwhelming developers. By establishing clear standards, you can make changes more straightforward.
The key is to design systems in a way that changes in one part—like the frontend or a specific service—don’t cascade into issues elsewhere.
A clear separation of concerns, such as having distinct tiers for frontend and backend, helps make adaptation easier. For example, updating the frontend should not require major backend changes if the architecture is well-structured.you can to make a change in the frontend alone instead of thinking of how it works with everything else.developers have a better focus on what they need to adapt too.
3. Security
Security is critical in architectural design. From securing APIs to managing authentication keys, safeguarding your system is non-negotiable. A breach or data leak could lead to significant financial and reputation losses for a company.
Building security into your design from the beginning, rather than as an afterthought, is always a better approach.
4. Technology choice
choosing the right technology stack for the system can be crucial and difficult. Have you used the technology in production? While new tech is cool and fun, if you can't support it or troubleshoot when errors happen, you could be setting yourself up for future problems.
It’s fine to experiment in side projects, but in production systems, you need to be a bit more serious with the technology choices you make because companies require reliable, well-supported technologies. The goal is to balance innovation with practicality.
5. Resource Management
Determining whether you are allocating the right resources for a system's development and maintenance can be challenging. Resources aren’t limited to cloud or memory; they also include developer time, management effort, engineering support, and overall project timelines.
Effective planning is crucial—not just for tracking expenditures but also for understanding how much developer time and effort are being invested in the system.
6. Stakeholder Alignment
Getting stakeholders to agree on the system’s design can be challenging, especially without clear communication about your decisions. Misalignment often happens when engineers skip sharing their reasoning and don’t involve key contributors, such as product managers, engineering leads, or other impacted teams, early enough.
Since architectural design impacts various parts of the system, it’s essential to align with all stakeholders early on. Creating a culture of documentation and open conversations builds trust and ensures everyone understands the approach.
Be prepared for pushback and ready to explain your choices. Helping stakeholders see your perspective fosters collaboration and leads to better outcomes.
Final Thoughts
These challenges highlighted how backend architecture goes beyond code—it’s about making thoughtful decisions that balance complexity, adaptability, and collaboration.